Django Project vs Django App
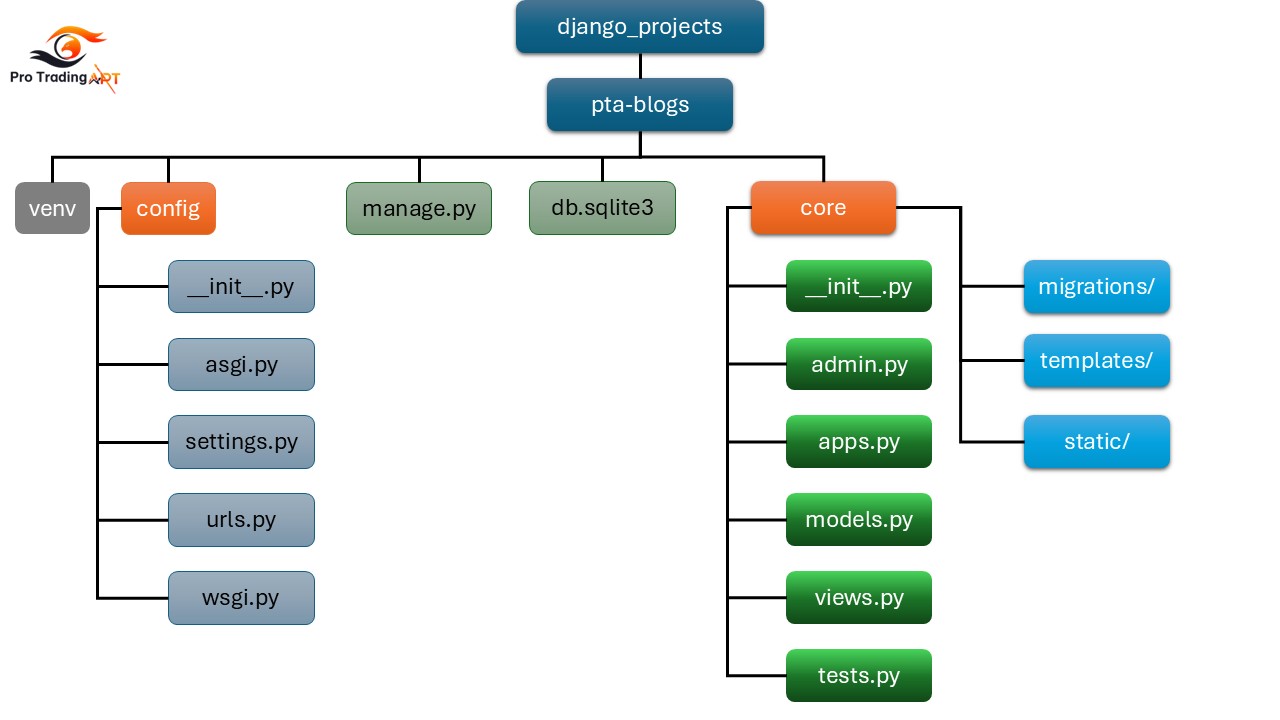
Django Project
A Django project includes the overall configuration and settings needed to run the entire web application.
Key Characteristics of a Django Project:
- Settings: Contains settings and configurations for the entire project, typically located in
settings.py. This includes database configurations, installed apps, middleware, static files, and more. - URLs: Manages URL routing for the entire project, typically in
urls.py. This file includes the URL patterns that direct HTTP requests to the appropriate views. - WSGI/ASGI Configuration: Includes
wsgi.pyorasgi.py, which serve as the entry points for the WSGI/ASGI servers to run the Django application. Structure:
pta-blogs/ manage.py config/ __init__.py settings.py urls.py wsgi.py
Django App
A Django app is a web application that performs a specific function or set of functions. An app is a self-contained module that can be included in any Django project. Django encourages a modular approach, where each app handles a distinct piece of the project's functionality.
Key Characteristics of a Django App:
- Modular and Reusable: Apps are designed to be modular and reusable. They can be easily plugged into different projects.
- Models: Contains model definitions for the data structures the app will use.
- Views: Contains view functions or classes that handle HTTP requests and return HTTP responses.
- Templates: Contains HTML templates used to render the views.
- Static Files: Includes static files (CSS, JavaScript, images) used by the app.
Structure:
core/ __init__.py admin.py apps.py models.py views.py tests.py migrations/ templates/ static/
Creating a Project and an App
Creating a Django Project:
django-admin startproject myprojectThis creates the project structure with the configuration files necessary to run the Django project.
Creating a Django App: Navigate into your project directory and create an app:
cd myproject python manage.py startapp myappThis creates the app structure within your project directory.
Adding the App to the Project: To include the app in your project, add it to the
INSTALLED_APPSlist insettings.py:# myproject/settings.py INSTALLED_APPS = [ ... 'myapp', ]Setting Up URLs: In your project's
urls.py, include the URLs from your app:# myproject/urls.py from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, include urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('myapp/', include('myapp.urls')), ]In your app, define the URLs in
urls.py:# myapp/urls.py from django.urls import path from . import views urlpatterns = [ path('', views.index, name='index'), ]
