QLineEdit: Allows single-line text editing
The QLineEdit widget in PySide6 provides a single-line text editor for user input. It is commonly used in forms and dialogs where users need to enter a single line of text, such as a name, password, or search query.
Key Features of QLineEdit
- Text Input: Allows users to input single-line text.
- Placeholders: Can display placeholder text when the input field is empty.
- Input Validation: Supports input masks and validators to control the input format.
- Echo Modes: Can hide input text for passwords or other sensitive information.
- Signals and Slots: Emits signals like
textChangedandeditingFinishedto handle text input events.
Creating a QLineEdit
To create a QLineEdit in PySide6, instantiate the QLineEdit class and add it to a layout. Here is a basic example:
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QLineEdit, QVBoxLayout, QWidget
class LineEditExample(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.line_edit = QLineEdit()
layout.addWidget(self.line_edit)
self.setLayout(layout)
self.setWindowTitle('QLineEdit Example')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication([])
app.setStyle("Fusion")
window = LineEditExample()
window.show()
app.exec()
In this example, a simple QLineEdit is created and added to a vertical layout.
Using Placeholder Text
You can set placeholder text in QLineEdit to give users a hint about what to enter:
self.line_edit.setPlaceholderText("Enter your text here")
Input Masks and Validators
Input masks and validators help control the format of the input. For example, to restrict the input to a phone number format:
self.line_edit.setInputMask("(+99) 9999999999")
For more complex validation, you can use validators:
from PySide6.QtGui import QIntValidator
self.line_edit.setValidator(QIntValidator(0, 100))
This validator restricts the input to integers between 0 and 100.
Echo Modes
Echo modes control how the input text is displayed. For example, to create a password input field:
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QLineEdit
self.line_edit.setEchoMode(QLineEdit.Password)
The QLineEdit supports several echo modes:
QLineEdit.Normal: Displays the text normally.QLineEdit.NoEcho: Does not display the text.QLineEdit.Password: Displays the text as asterisks.QLineEdit.PasswordEchoOnEdit: Displays the text as asterisks, but shows the actual text while editing.
Handling Signals
The QLineEdit emits several signals that you can connect to custom slot functions. The most commonly used signals are textChanged and editingFinished:
self.line_edit.textChanged.connect(self.on_text_changed)
self.line_edit.editingFinished.connect(self.on_editing_finished)
def on_text_changed(self, text):
print(f"Text changed: {text}")
def on_editing_finished(self):
print("Editing finished")
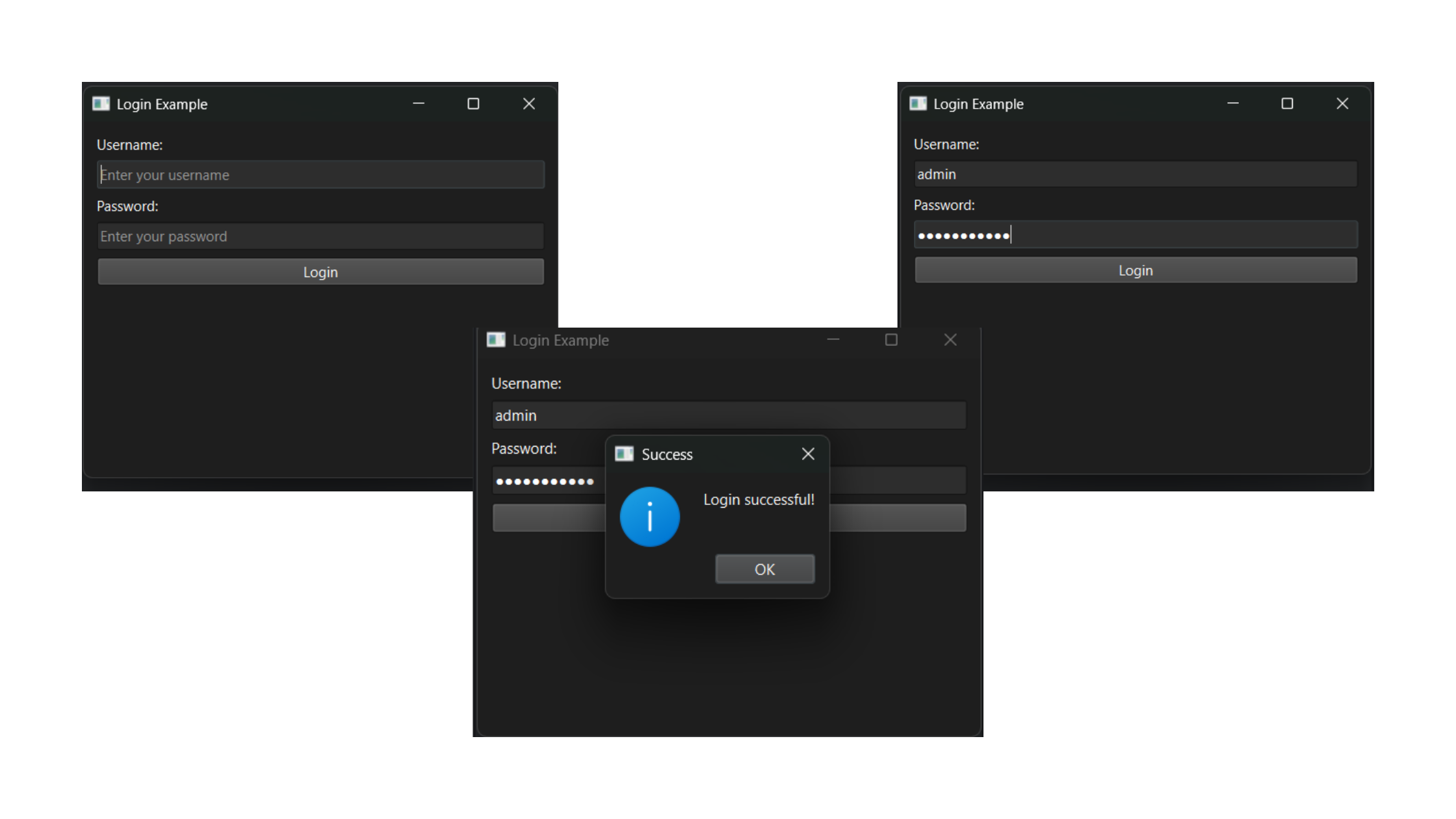
Practical Example
Let's create a more practical example where the QLineEdit is used to input a username and a password:
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QLineEdit, QLabel, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QPushButton, QMessageBox, \\
QSpacerItem, QSizePolicy
class LoginExample(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle('Login Example')
self.setMinimumSize(400, 300)
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.username_label = QLabel("Username:")
self.username_edit = QLineEdit()
self.username_edit.setPlaceholderText("Enter your username")
self.password_label = QLabel("Password:")
self.password_edit = QLineEdit()
self.password_edit.setPlaceholderText("Enter your password")
self.password_edit.setEchoMode(QLineEdit.Password)
self.login_button = QPushButton("Login")
self.login_button.clicked.connect(self.login)
layout.addWidget(self.username_label)
layout.addWidget(self.username_edit)
layout.addWidget(self.password_label)
layout.addWidget(self.password_edit)
layout.addWidget(self.login_button)
# Add vertical spacer at the bottom to push content up
spacer = QSpacerItem(20, 40, QSizePolicy.Minimum, QSizePolicy.Expanding)
layout.addItem(spacer)
self.setLayout(layout)
def login(self):
# Dummy data for validation
dummy_username = "admin"
dummy_password = "password123"
entered_username = self.username_edit.text()
entered_password = self.password_edit.text()
if entered_username == dummy_username and entered_password == dummy_password:
QMessageBox.information(self, "Success", "Login successful!")
else:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "Error", "Invalid username or password.")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication([])
app.setStyle("Fusion")
window = LoginExample()
window.show()
app.exec()
In this example, we create a simple login form with two QLineEdit widgets, one for the username and one for the password. The password field hides the input text for security.
